C# Professional - Numbers
Open Source Your Knowledge, Become a Contributor
Technology knowledge has to be shared and made accessible for free. Join the movement.

Arithmetic Overflow
Overflow is an operation that occurs when a calculation produces a result that is greater in magnitude than that which a given register or storage location can store or represent.
See this example of overflow:
Detecting & Catching Overflows
As you can see, when reaching the maximum value of a given numeric type, trying to add anything will overflow the capacity and result in a wrong value.
By default, the .Net runtime will not raise exceptions when doing numeric calculations. If you want to ensure that arithmetic operations will throw overflow exceptions if an overflow happens, you need to use the checked { ... } code block.
When using the checked { ... } code block, if any arithmetic operation causes an overflow, an OverflowException will be thrown, and will need to be catched and handled.
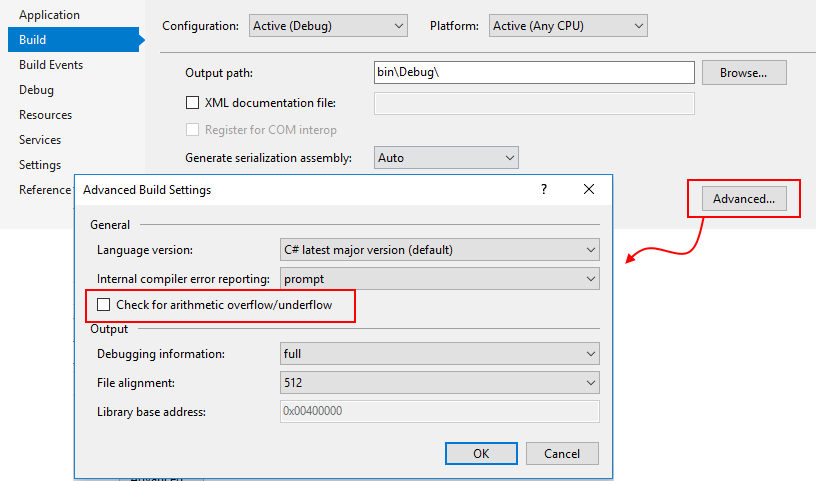
Note: Depending on the build options of your project, detection of overflow and underflow can be automatically enabled, removing the need for the checked { ... } code block. The option can be activated in the "Advanced" build settings of any C# project.
Note: Overflows can also happen when the result is smaller than the smallest value that can be stored or represented. These are often called underflows. The result of the operation when not using the checked { ... } code block is zero.